Physics:Extended theories of gravity
Extended theories of gravity are alternative theories of gravity developed from the exact starting points investigated first by Albert Einstein and Hilbert. These are theories describing gravity, which are metric theory, "a linear connection" or related affine theories, or metric-affine gravitation theory. Rather than trying to discover correct calculations for the matter side of the Einstein field equations; which include inflation, dark energy, dark matter, large-scale structure, and possibly quantum gravity; it is proposed, instead, to change the gravitational side of the equation.[1][2]
Proposed theories
Hernández et al.
 | This article may lend undue weight to certain ideas, incidents, or controversies. (October 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
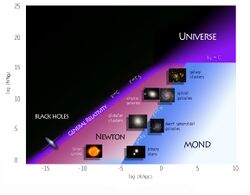
One such theory is also an extension to general relativity and Newton's Universal gravity law ([math]\displaystyle{ f(\chi)=\chi^\frac{3}{2} }[/math]), first proposed in 2010 by the Mexican astronomers Xavier Hernández Doring, Sergio Mendoza Ramos et al., researchers at the Astronomy Institute, at the National Autonomous University of Mexico.[3][4] This theory is in accordance with observations of kinematics of the solar system, extended binary stars,[5] and all types of galaxies and galactic groups and clouds.[6] It also reproduces the gravitational lensing effect without the need of postulating dark matter.[7]
There is some evidence that it could also explain the dark energy phenomena[8] and give a solution to the initial conditions problem.[9]
These results can be classified as a metric f(R) gravity theory, more properly an f(R,T) theory, derived from an action principle. This approach to solve the dark matter problem takes into account the Tully–Fisher relation as an empirical law that applies always at scales larger than the Milgrom radius.[10]
See also
- Modified Newtonian Dynamics
- Alternatives to general relativity
References
- ↑ Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. (2011). "Extended Theories of Gravity". Physics Reports 509 (4–5): 167–321. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2011.09.003. Bibcode: 2011PhR...509..167C.
- ↑ Capozziello, S.; Francaviglia, M. (2008). "Extended theories of gravity and their cosmological and astrophysical applications". General Relativity and Gravitation 40 (2–3): 357–420. doi:10.1007/s10714-007-0551-y. Bibcode: 2008GReGr..40..357C.
- ↑ Mendoza, S.; Hernandez, X.; Hidalgo, J. C.; Bernal, T. (2011). "A natural approach to extended Newtonian gravity: Tests and predictions across astrophysical scales". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 411 (1): 226–234. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17685.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.411..226M.
- ↑ Hidalgo, J. C.; Mendoza, S.; Hernandez, X.; Bernal, T.; Jimenez, M. A.; Allen, C. (2012). "Non-relativistic Extended Gravity and its applications across different astrophysical scales". AIP Conference Proceedings 1458: 427–430. doi:10.1063/1.4734451. Bibcode: 2012AIPC.1458..427H.
- ↑ Hernandez, X.; Jiménez, M. A.; Allen, C. (2012). "Wide binaries as a critical test of Classical Gravity". European Physical Journal C 72 (2): 1884. doi:10.1140/epjc/s10052-012-1884-6. Bibcode: 2012EPJC...72.1884H.
- ↑ Hernandez, X. (2012). "A Phase Space Diagram for Gravity". Entropy 14 (12): 848. doi:10.3390/e14050848. Bibcode: 2012Entrp..14..848H.
- ↑ Mendoza, S.; Bernal, T.; Hernandez, X.; Hidalgo, J. C.; Torres, L. A. (2013). "Gravitational lensing with f(χ)=χ3/2 gravity in accordance with astrophysical observations". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 433 (3): 1802–1812. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt752. Bibcode: 2013MNRAS.433.1802M.
- ↑ Carranza, D. A.; Mendoza, S.; Torres, L. A. (2012). "A cosmological dust model with extended f(χ) gravity". European Physical Journal C 73: 2282. doi:10.1140/epjc/s10052-013-2282-4. Bibcode: 2013EPJC...73.2282C.
- ↑ Hernandez, X.; Jimenez, M. A. (2013). "A first linear cosmological structure formation scenario under extended gravity". arXiv:1307.0777 [astro-ph.CO].
- ↑ Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. (2013). "Extended Gravity: State of the Art and Perspectives". in Rosquist, K.; Jantzen, R. T.; Ruffini, R.. World Scientific. Bibcode: 2013arXiv1307.4523C.
Further reading
- Wands, D. (1994). "Extended gravity theories and the Einstein–Hilbert action". Classical and Quantum Gravity 11 (1): 269–279. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/11/1/025. Bibcode: 1994CQGra..11..269W.
- Allemandi, G.; Capone, M.; Capozziello, S.; Francaviglia, M. (2006). "Conformal aspects of the Palatini approach in Extended Theories of Gravity". General Relativity and Gravitation 38 (1): 33–60. doi:10.1007/s10714-005-0208-7. Bibcode: 2006GReGr..38...33A.
External links
News
- El universal.com (in Spanish).
- La jornada.mx (in Spanish).
- La crónica.com (in Spanish).
 |